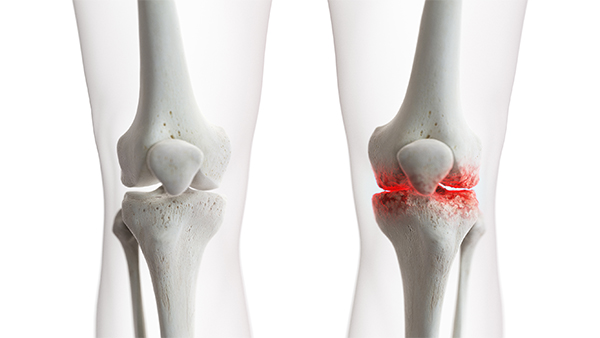
Knee Arthritis
Signs, Symptoms and Treatment
About Arthritis
Arthritis means inflammation of the joints and causes varying degrees of pain and stiffness. Arthritis can make it difficult to do daily activities and can stop you from walking comfortably or sitting up straight. There are many different forms of arthritis and each one causes different symptoms and needs different treatments.
Our treatment goals are to improve quality of life by reducing pain, restoring function, correcting deformity and keeping you MOVING.
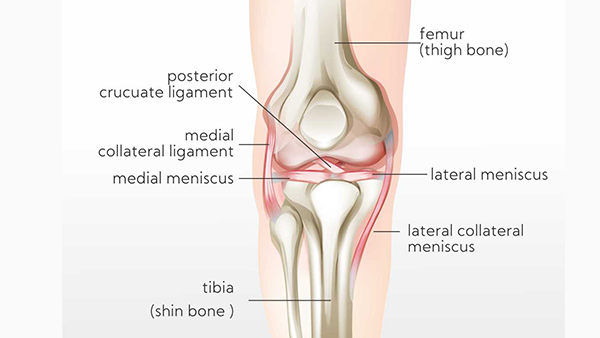
About the Knee Joint
The knee joint is made up of three bones, the bottom part of the thighbone (femur), the top part of the shinbone (tibia) and the kneecap (patella). A layer of articular cartilage covers the surfaces of these parts of the bone to form the knee joint, cushioning the joint and enabling it to glide together easily. Once arthritis occurs, a loss of cartilage ensues leading to bone-on-bone contact which causes damage to the bone, inflammation and a great degree of pain and discomfort.
The most common type of arthritis that can affect the knee is primary osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative arthritis. It is associated with wear and tear of the knee joint as you get older and can affect you especially if there is a family history of it.
The Risks of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis affects your quality of life, mobility and your overall health. Failure to treat osteoarthritis of the knee raises your risk of heart disease, diabetic complications and death.
Other causes/types of Knee arthritis include
Post-traumatic arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis occurs after you’ve experienced a trauma to a joint and develops quicker than the usual period of wear and tear arthritis.
Avascular necrosis of the knee (AVN)
Avascular necrosis of the knee (AVN) is a condition where the blood supply to any part of the bones that make up the knee joint is disrupted. If left untreated the bone dies and the knee degenerates causing arthritis.
Deformity of the legs
Deformity of the legs: excessive valgus deformity (knock knee) or varus deformity (bow leg) can cause excess stress in a certain part of the knee increasing the risk of arthritis
Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis is due to a bacterial infection within the knee joint and is more common in children. This type of arthritis requires emergency surgical drainage of the knee joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis: this is an autoimmune disease, which means the body’s immune system attacks the soft tissue lining of the joints causing painful inflammation and swelling. Over time, this results in bone erosion and joint deformity.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus is an autoimmune disease which causes inflammation and damage to the knee joint, causing knee arthritis.
Sings and Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
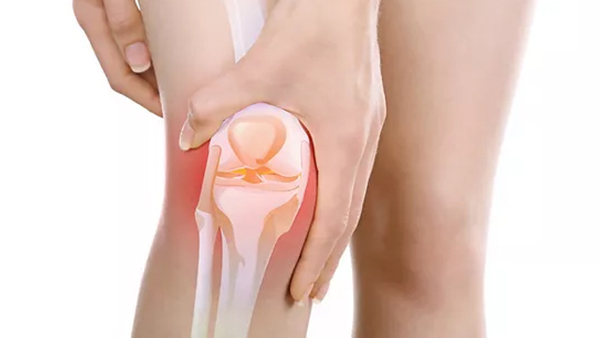
Knee Arthritis Symptoms
- Pain in the knee especially with certain movements.
- Stiffness making it difficult to bend and straighten the knee.
- Crepitus, which is the crunching, snapping and clicking sound when moving.
- Knee buckling
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty with ADL (activities of daily living)
- Difficulty doing stairs
Knee Arthritis Treatment Options
Is there a cure for Knee Arthritis?
There are no cures for knee arthritis, but there are steps that can be taken to ease the symptoms and slow down the progression of this disease. It is important to recognise it early and treat it accordingly.
It is essential to keep your joints healthy by maintaining mobility and function therefore enabling a frictionless joint motion. Knee arthritis can be treated both surgically and non-surgically.

Physical therapy
Physical therapy under the guideance of a physio therapist.

Exercising (low impact)

Walking Aids
Walking aids such as canes that provide safety and ease while walking.

Joint Support
Wearing a knee sleeve or brace
Weight Loss (if applicable)
Excess weight places strain on your joints. A weight loss program can help in the prevention and recovery of knee arthritis.
Anti-inflammatory medications
Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, Celebrex and Arcoxia.

Injections
- Corticosteroids injections that block the inflammation in the joint providing pain relief.
- PRP (platelet rich plasma)
- Viscosupplementation (injecting special gels into the knee)
Surgical Options for Knee Arthritis
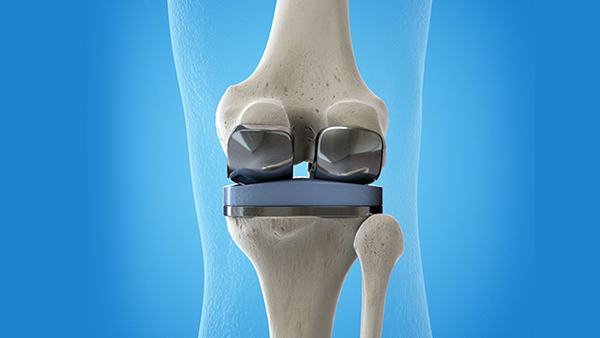
Total knee replacement
Total knee replacements (Arthroplasty) using metal and plastic parts remains the gold standard in treating end stage knee osteoarthritis.
Knee Osteotomy
Knee Osteotomy (Tibial or Femoral Osteotomy) preserves the native knee joint and is for patients that have experienced wear and tear on one side of their knee joint and have poor knee alignment. A piece of natural bone or artificial bone material is either removed or added to realign the mechanical axis of the limb and shift pressure onto the good side of the knee reducing pressure on the bad side.
Partial knee replacement
Partial knee replacement (Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty) which replaces only one of the knee’s three compartments. This option is applicable in the earlier stages of the disease. Patients need to fulfill very strict criteria to be considered for a partial knee replacement. The pain is usually less and the recovery faster with this procedure.
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy involves inserting a camera into the knee and cleaning out diseased areas in the hope of providing short term pain relief
Cartilage repair and restoration
Cartilage repair and restoration procedures are indicated in patients who have a small and isolated area of articular cartilage damage and are performed with the aim of slowing down or preventing severe arthritis.
